Composite two images according to a mask image with Python, Pillow
The Image module of the image processing library Pillow (PIL) of Python provides composite() for compositing two images according to a mask image.
This article describes the following contents.
- Parameters of
Image.composite() - Sample code of
Image.composite()- Composite the whole area at a constant ratio
- Create mask image by drawing
- Use existing image as mask image
Please refer to the following article for the installation and basic usage of Pillow (PIL).
Note that composite() is a function to composite two images of the same size. Use the paste() to composite images of different sizes. paste() allows you to mask a small image and paste it anywhere on the large image.
Image composition is possible with OpenCV and NumPy instead of Pillow. See the article below.
Parameters of Image.composite()
There are three parameters for composite(). All three must be Image objects, all of the same size.
image1, image2
Two images to composite.
mask
Mask image.
mode must be one of the following three types.
1: 1 bit image (binary image)L: 8-bit grayscale imageRGBA: Image with alpha channel
image1 and image2 are alpha-blended according to the value of mask.
# For 1bit
result = mask * image1 + (1 - mask) * image2
# For 8bit
result = mask / 255 * image1 + (1 - mask / 255 ) * image2
Sample code of Image.composite()
Import Image from PIL and load images.
ImageDraw and ImageFilter are used when drawing a figure and creating a mask image. When reading an image file and using it as a mask image, they may be omitted.
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFilter
im1 = Image.open('data/src/lena.jpg')
im2 = Image.open('data/src/rocket.jpg').resize(im1.size)


This time, the second image is reduced by resize() to match the size. If you cut out part of the image and adjust the size, use crop(). See the following article.
Composite the whole area at a constant ratio
When a solid image is used as a mask image, the entire image is composited at a constant ratio.
As an example, create a solid image with a value of 128 with Image.new() and use it as a mask image.
mask = Image.new("L", im1.size, 128)
im = Image.composite(im1, im2, mask)
# im = Image.blend(im1, im2, 0.5)

blend() method can also composite the entire surface at a constant ratio. Specify a constant of 0.0 to 1.0 as the parameter alpha instead of mask.
Create mask image by drawing
If you want to mask and composite with a simple shape, such as circle and rectangle, drawing with ImageDraw module is convenient. For details on drawing, see the following article. You can also draw polygons.
Draw a white circle on a black background to create a mask image.
mask = Image.new("L", im1.size, 0)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(mask)
draw.ellipse((140, 50, 260, 170), fill=255)
im = Image.composite(im1, im2, mask)
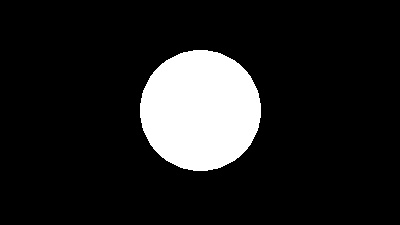

The boundaries can be composited smoothly by blurring the mask image with ImageFilter.
mask_blur = mask.filter(ImageFilter.GaussianBlur(10))
im = Image.composite(im1, im2, mask_blur)


Use existing image as mask image
An existing image can be read and used as a mask image to composite in a complex shape.
Try using a black and white horse-shaped image (scikit-image sample: skimage.data.horse()).
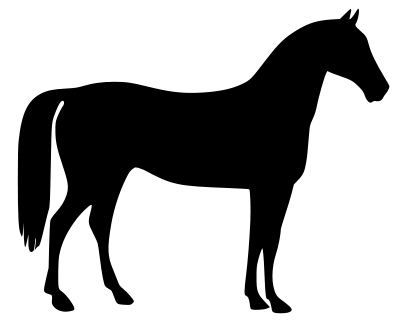
After the image is read by open(), it is adjusted to the size of the pasted image by resize(), and the mode is converted to 'L' (grayscale) by convert().
mask = Image.open('data/src/horse.png').convert('L').resize(im1.size)
im = Image.composite(im1, im2, mask)

If you want to reverse the black and white of the mask image, please refer to the following article.
Another example:
It is composited to change gradually with the gradation image generated using NumPy.
mask = Image.open('data/src/gradation_h.jpg').convert('L').resize(im1.size)
im = Image.composite(im1, im2, mask)

