Create transparent png image with Python, Pillow (putalpha)
Image module of the Python image processing library Pillow (PIL) provides putalpha() for adding an alpha channel to an image.
This article describes the following contents.
- How to use
Image.putalpha() - Set uniform transparency over the entire surface
- Create an alpha channel with
ImageDraw - Use the existing image as an alpha channel
Please refer to the following article for the installation and basic usage of Pillow (PIL).
Import Image from PIL and load the original image.
ImageDraw and ImageFilter are used to draw shapes and create alpha channels. They may be omitted if the image file is read and used as an alpha channel.
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFilter
im_rgb = Image.open('data/src/lena.jpg')

How to use Image.putalpha()
The parameter of putalpha() is only alpha. As it is literally put the alpha channel layer to the original image.
If mode of the original image is RGB (8 bit x 3: full color) or L (8 bit x 1: black and white), an alpha channel is newly added, and if RGBA or LA, the original alpha channel is updated.
Specified by a constant
When an integer value of 8 bits (0 to 255) is set to alpha, the transmittance according to the value is set on the entire surface.
0 means 100% transparency, 255 means 0% transparency (no transparency).
Specified by Image object
If you set an Image object of the same size as the original image in mode='L' (8-bit grayscale) to alpha, you can set the alpha channel to various shapes.
As in the constant case, 0 means 100% transparency, 255 means 0% transparency (no transparency).
Set uniform transparency over the entire surface
If you set an integer value to alpha, the transparency according to the value will be set on the entire surface.
Note that putalpha() overwrites the original image, so if you want to keep the original image as it is, use the one copied with copy().
im_rgba = im_rgb.copy()
im_rgba.putalpha(128)
im_rgba.save('data/dst/pillow_putalpha_solid.png')

In this example, alpha=128 gives about 50% transparency (128 / 255 ~ 50%).
Create an alpha channel with ImageDraw
If you want to add an alpha channel with a simple shape, such as a circle or rectangle, drawing in the ImageDraw module is useful. For details on drawing, see the following article. You can also draw polygons.
Draw a white circle on a black background and set it to the alpha channel.
im_a = Image.new("L", im_rgb.size, 0)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(im_a)
draw.ellipse((140, 50, 260, 170), fill=255)
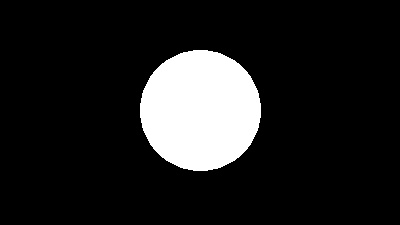
im_rgba = im_rgb.copy()
im_rgba.putalpha(im_a)
im_rgba_crop = im_rgba.crop((140, 50, 260, 170))
im_rgba_crop.save('data/dst/pillow_putalpha_circle.png')

You can use ImageFilter to smooth out the boundaries.
im_a_blur = im_a.filter(ImageFilter.GaussianBlur(4))

im_rgba = im_rgb.copy()
im_rgba.putalpha(im_a_blur)
im_rgba_crop = im_rgba.crop((135, 45, 265, 175))
im_rgba_crop.save('data/dst/pillow_putalpha_circle_blur.png')

In each example, the outside of the circle is trimmed to a rectangle with crop(). See the following article for crop().
Use the existing image as an alpha channel
You can load an existing image and set it as an alpha channel.
Try using a black and white horse-shaped image (scikit-image sample: skimage.data.horse()).
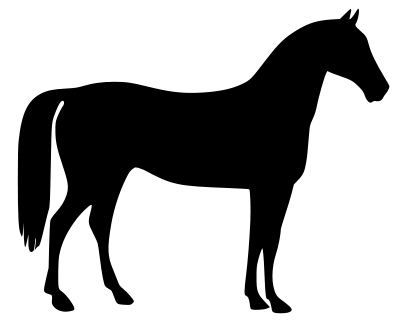
In this example, to leave the image horse-shaped, use an image with a white horse and a black background (an inverted image).
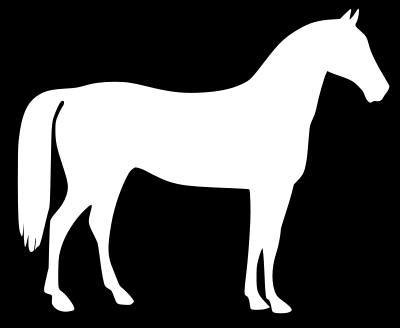
After the image is read by open(), it is adjusted to the size of the pasted image by resize(), and the mode is converted to 'L' (grayscale) by convert().
im_a = Image.open('data/src/horse_r.png').convert('L').resize(im_rgb.size)
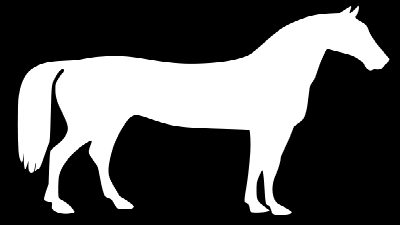
im_rgba = im_rgb.copy()
im_rgba.putalpha(im_a)
im_rgba.save('data/dst/pillow_putalpha_horse.png')
